Material of PVB Films
PVB films, also called polyvinylbutyral films, are an extruded mixture of special plasticizer, additives, and PVB resin, forming PVB films with an even thickness.
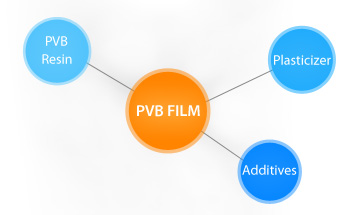
Structure Compositions of PVB Films
PVB films are primarily applied in laminated glass that is a construction of two or more pieces of glass. The high adhesive PVB films are clamped between layers, so PVB films must equip with excellent adhesion, light transmission and safety. 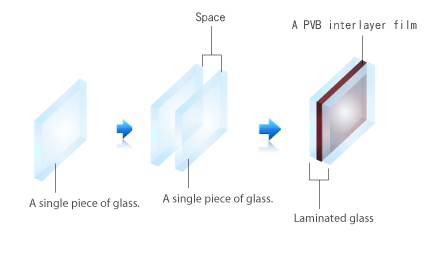
The advantages and characteristics of PVB films
-
High safety building material:
-
Due to high tenacity and adhesion of PVB films, the films can endure external impact and are hard to penetrate through. Although the glass might be broken, the broken glass pieces will not scatter around, reducing damage level dramatically.
-
High energy saving building material:
-
PVB films can reduce radiations from the sun to penetrate into buildings and automobiles, which can balance the high temperature sunlight, saving electricity consumption for air-conditioning in buildings and automobiles effectively.
-
Soundproof:
-
PVB films have a good characteristic of Soundproof, which not only block external noise but also provide a private space.
-
Absorption of UV rays:
-
PVB films have a good characteristic of UV rays absorption, preventing discoloration due to UV rays from the sun.
-
Aesthetics of buildings:
-
PVB films provide multiple colors to choose from, harmonizing with the surroundings and meeting the designing demand.
Applications of laminated glass
|
Types of plastic
|
Image |
Abbreviation |
Polymer name |
Uses |
 |
PETE or PET |
Polyethylene
terephthalate |
Polyester fibres, thermoformed sheet, strapping, and soft drink bottles. (See also: Recycling of PET bottles) |
 |
HDPE or PEHD |
High-density
polyethylene |
Bottles, grocery bags, milk jugs, recycling bins, agricultural pipe, base cups, car stops, playground equipment, and plastic lumber. |
 |
PVC or V |
Polyvinyl chloride |
Pipe, fencing, shower curtains, lawn chairs, non-food bottles and children's toys. |
 |
LDPE or PEBD |
Low density
polyethylene |
Plastic bags, 6 pack rings, various containers, dispensing bottles, wash bottles, tubing, and various molded laboratory equipment. |
 |
PP |
Polypropylene |
Auto parts, industrial fibers, food containers, and dishware. |
 |
PS |
Polystyrene |
Desk accessories, cafeteria trays, plastic utensils, toys, video cassettes and cases, clamshell containers, packaging peanuts, and insulation board and other expanded polystyrene products. (e.g., Styrofoam) |
 |
OTHER |
Other plastics,
including acrylic,
fiberglass, nylon,
polycarbonate,
and polylactic acid
(a bioplastic),
and multilayer
combinations of
different plastics |
Bottles, plastic lumber applications, Headlight lenses, and safety shields/glasses. |
|
Applications of ethylene
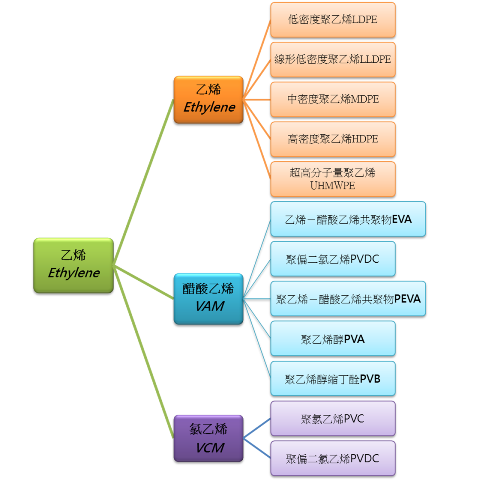
乙烯 Ethylene :
-
低密度聚乙烯、高 聚乙烯 Low Density Polyethylene(LDPE)
-
線形低密度聚乙烯 Linear Low Density Polyethylene(LLDPE)
-
中密度聚乙烯、 峰 脂 Medium Density Polyethylene(MDPE)
-
高密度聚乙烯、低 聚乙烯 High Density Polyethylene(HDPE)
-
超高分子量聚乙烯 Ultra High Molecuar Weight Polyethylene(UHMWPE)
-
醋酸乙烯 Vinyl Acetate Monomer (VAM)
-
乙烯-醋酸乙烯共聚物 ethylene vinyl acetate (EVA), used in films, wire coating and adhesives
-
聚乙烯-醋酸乙烯共聚物polyethylene vinyl acetate (PEVA) a copolymer of polyethylene and EVA used in shower curtains, body bags
-
聚乙烯醇polyvinyl acetate (PVA), used in paints and adhesives, such as white glue
-
聚乙烯醇縮丁醛 polyvinyl butyral (PVB), used in safety glass films.
-
氯乙烯Vinyl Chloride Monomer (VCM)
-
聚氯乙烯polyvinyl chloride (PVC)
-
聚偏二氯乙烯polyvinylidene chloride (PVDC)
Graphic :
Polyethylene property :
|
泛用聚乙烯
PE
|
密度density
(g/cm3)
|
軟化點
Softening Point (℃)
|
|
低密度聚乙烯LDPE
|
0.91~0.93
|
105~115
|
|
線形低密度聚乙烯LLDPE
|
0.915~0.94
|
120~125
|
|
中密度聚乙烯MDPE
|
0.926~0.94
|
126-135
|
|
高密度聚乙烯HDPE
|
0.945~0.976
|
125~137
|
Reference source : http://www.ides.com/info/generics/27/Polyethylene-PE
|
Polypropylene PP:
-
INTRODUCTION:
-
Polypropylene (PP) is a linear hydrocarbon polymer, expressed as CnH2n. PP, like polyethylene (see HDPE, L/LLDPE) and polybutene (PB), is a polyolefin or saturated polymer. Polypropylene is one of those most versatile polymers available with applications, both as a plastic and as a fiber, in virtually all of the plastics end-use markets.
-
PROPERTIES:
-
(Semi-rigid, translucent, good chemical resistance, tough, good fatigue resistance, integral hinge property, good heat resistance). Production of polypropylene takes place by slurry, solution or gas phase process, in which the propylene monomer is subjected to heat and pressure in the presence of a catalyst system. Polymerisation is achieved at relatively low temperature and pressure and the product yielded is translucent, but readily coloured. Differences in catalyst and production conditions can be used to alter the properties of the plastic.
PP does not present stress-cracking problems and offers excellent electrical and chemical resistance at higher temperatures. While the properties of PP are similar to those of Polyethylene, there are specific differences. These include a lower density, higher softening point (PP doesn't melt below 160oC, Polyethylene, a more common plastic, will anneal at around 100oC) and higher rigidity and hardness. Additives are applied to all commercially produced polypropylene resins to protect the polymer during processing and to enhance end-use performance.
GRADES AVAILABLE:
Three types of polypropylene are currently available. Each suits particular specifications and costing (although there is often some overlap). Homopolymers - A General Purpose Grade that can be used in a variety of different applications. Block copolymers - incorporating 5-15% ethylene, have much improved impact resistance extending to temperatures below -20oC. Their toughness can be further enhanced by the addition of impact modifiers, traditionally elastomers in a blending process. Random copolymers - incorporate co-monomer units arranged randomly (as distinct from discrete blocks) along the polypropylene long chain molecule. Such polymers typically containing 1-7% ethylene are selected where a lower melting point, more flexibility and enhanced clarity are advantageous. Different PP grades are available dependent on the application and chosen processing method.
-
PHYSICAL PROPERTIES:
-
Tensile Strength 0.95 - 1.30 N/mm²
Notched Impact Strength 3.0 - 30.0 Kj/m²
Thermal Coefficient of expansion 100 - 150 x 10-6
Max Cont Use Temp 80 oC
Density 0.905 g/cm3
-
RESISTANCE TO CHEMICALS:
-
Dilute Acid ****
Dilute Alkalis ****
Oils and Greases ** variable
Aliphatic Hydrocarbons *
Aromatic Hydrocarbons *
Halogenated Hydrocarbons *
Alcohols ****
KEY * poor ** moderate *** good **** very good
APPLICATIONS:
Polypropylene can be processed by virtually all thermoplastic-processing methods. Most typically PP Products are manufactured by: Extrusion Blow Moulding, Injection Moulding, and General Purpose Extrusion. Expanded Polypropylene (EPP) may be moulded in a specialist process.
Flexible Packaging:
PP is one of the leading materials used for film extrusion and has in recent years benefited versus cellophane, metals and paper on account of its superior puncture resistance, low sealing threshold and competitive price. PP Film is available either as Cast Film or bi-axially orientated PP (BOPP).
-
The film market may be divided in to three main sectors:
-
Food and Confectioneries
Tobacco
Clothing
The food and confectioneries sector is the largest of the film markets with usage ranging from confectioneries to crisps and biscuits. Tobacco products represent a significant market for PP (second largest after food and confectioneries). Rigid packaging subdivides into a multitude of packaging applications from caps and closures to pallets and crates.
Rigid Packaging:
Reusable and collapsible/stackable crates are a great application for PP, providing ease to transport (both full and empty) and allow simple, safe and efficient storage of products and are ideal for Just-in-Time (JIT) storage solutions. As a consequence, supermarkets are beginning to revert to use and similar products are finding application in the automotive supply chain.
Caps and Closures manufactured of PP have benefited from growth in the PET bottle market, particularly for mineral water containment and that of edible oil.
PP is blow moulded to produce bottles for the packaging of a range of products including condiments, detergent and toiletries markets,PP thin-walled containers (e.g. yoghurt pots) are also common. PP competes with PS in this field, offering a cheaper material option (processing costs can, however, offset this benefit). PP is semi-crystalline product and consequently has a narrower processing window than PS and tends to display higher shrinkage. Modern thermoforming machinery is capable (with two sets of tools) of processing either PP or PS, consequently the future infiltration of PP is very much dependent on price fluctuations.
Automotive:
In the automotive sector PP is utilised as a monomaterial solution for automotive interiors. The monomaterial dashboard is becoming increasingly achievable, PP film cushioning, film skins, and powder slush moulding and even blow moulded parts with integral PP textile covers are emerging.
Bumpers, cladding, and exterior trim are also available manufactured from polypropylene. Polypropylene developed for such applications provides low coefficient of linear thermal expansion and specific gravity, high chemical resistance and good weatherability, processability and impact/stiffness balance. Improvements with colour-at-the-press and pre-coloured PP have also reduced or eliminated the need for painting in some applications.
-
Consumer Products:
-
Products classified in this sector are Housewares, Furniture, Appliances, Luggage, Toys, Battery Cases and other "durable" items for home, garden or leisure use. Injection Moulding dominates the conversion process used for these products.
-
Fibre:
-
PP Fibre is utilised in a host of applications including tape, strapping, bulk continuous filament, staple fibres, spunbound, and continuous filament.
-
Industrial:
-
PP is used to manufacture a range of Sheet, Pipe, Compounding and Returnable Transport Packaging (RTP). With the exception of RTP where Injection Moulding is used, extrusion dominates the conversion process used for these products. Some PP is utilised by the construction sector, most notable domestic drainage pipes.
Source- The British Plastics Federation
|
|
